Contents
Procurement Management: A Guide to the Basics of the Procurement Cycle

Vlad Falin
•
•
Picture handling hundreds of weekly purchase requests from different departments, each demanding new vendor searches. When you finally make purchases after going through the cycle of approvals and negotiations, you end up facing goods and invoice discrepancies.
That’s a chaotic situation you certainly want to avoid.
While procurement may seem like a simple purchase on paper, the process requires planning and structure for larger organizations.
One way to avoid this chaos is through procurement management, which helps businesses streamline the acquisition and record-keeping process. This reduces overhead costs and helps you remain profitable.
In this post, we will explore what is procurement management, outline the steps involved, and give tips to optimize your procurement cycle for an effective procurement management system.
What is Procurement Management?
Procurement management refers to the strategic acquisition of goods and services to meet the needs of an organization. It covers the entire goods procurement process from raising purchase requests to settling payments with vendors. This involves the procurement team’s planning, sourcing, negotiating, validating, and clearing payments to ensure a proper supply chain.
Steps Involved in the Procurement Management System

A standard procurement management process is intricate and involves several stakeholders. Here are the key steps:
- Needs Assessment: Identify internal requirements through meticulous forecasting.
- Vendor Selection and Database Establishment: Thoroughly vet vendors, creating a robust database for strategic partnerships.
- Negotiation of Terms: Engage in negotiations on pricing and delivery schedules to optimize resource utilization.
- Purchase Order Generation: Transform approved purchase requests into precise orders to minimize potential errors.
- Goods Receipt and Matching: Validate received goods against purchase orders (GRN matching) to ensure order accuracy and quality control.
- Invoice Approval and Payment Processing: Ensure accuracy before approving invoices and proceeding with payments.
- Record Maintenance for Auditing: Systematically document all transactions for transparent auditing, ensuring compliance and accountability.
Although the process looks simple, it has several loopholes. There are numerous steps involved, and the entire process becomes tricky to execute. These steps are scattered across multiple platforms, complicating reconciliation during the audit season.
Furthermore, it requires approvals at certain stages, making it unfavorable for larger teams with complex hierarchies.
How to Optimize the Procurement Management System
You can overcome these challenges by automating your systems.
Automation makes this lengthy and complex process a simple and efficient procurement cycle. The employees get a dedicated platform to raise requests. Furthermore, stakeholders can efficiently review and approve requests with automated notifications.
Automation also simplifies GRN matching through the data stored in the software. Accounting and payment integrations help clear approved invoices within seconds.
Throughout this process, you gain real-time visibility and control over expenses. Moreover, having all your information on a unified platform simplifies reconciliation and ensures a proper audit trail.
Here are five ways automating the procurement process helps your business:
1. Internal Control Over Financial Reporting (ICFR)
Automation ensures compliance with ICFR standards and upholds quality controls throughout the procurement process. It does this by using trigger-based approval workflows that follow predefined financial controls. It implements validation checks to ensure that procurement transactions meet quality control standards. This makes two-way and three-way matching seamless.
By deploying a single software solution, you detect and prevent potential errors or discrepancies in financial reporting.
2. Documentation
Automation brings together purchase requests, purchase orders, receipts, and all the relevant conversations on a unified platform. This makes storing and retrieving information easier, especially during the audit season. Also, optical character recognition (OCR) technology simplifies extracting key information, eliminating the need for manual data entry.
As a result, you improve document accuracy and prevent errors such as late or incorrect returns due to missing receipts, invoices, payables, and supporting documentation.
3. Integration
Automation software integrates with your accounting software, payment gateways, and ERPs bringing together the scattered pieces of procurement.
It allows you to request, manage, match goods receipts, and pay vendors from a single place. The best part is that your data remains consistent across all your software making the lives of financial controllers easier.
4. Measure
Automation offers you real-time visibility through a custom dashboard. It gives you a holistic view of the procure-to-pay process with a centralized data repository.
This makes it easier to extract insights and optimize the process to improve margins, such as average payables due, top vendors, department-wise expenses, etc.
5. Standardize Workflows
Automation helps you create standardized workflows to ensure consistency and efficiency. As a result, each stakeholder gets notified to complete their part. So, be it approving expenses or GRN matching, these set workflows eliminate the need to chase employees averting potential delays.
Challenges of Automating the Procurement Cycle
While automation does offer several benefits, choosing the right tool is crucial. One wrong decision and you might end up in one of the following situations:
- You invest in a basic software that lacks functionality and doesn’t solve your procurement issues.
- You choose a complex product that is difficult to understand and operate.
- You get a tool that doesn’t integrate with your existing accounting and payment software, increasing the manual task of syncing data across these systems.
- You get multiple products for different steps that lack integration, hindering efficient and streamlined procurement management.
Automation becomes a nightmare with the wrong software. All these scenarios lead to resource wastage. Moreover, weeks and months spent on implementation disrupt the supply chain.
What a Good Automation Procurement Management System Looks Like
Here’s how a comprehensive automation platform makes your procurement process easy, functional, flexible, and scalable.
1. Standardize Process

You have a centralized platform to consolidate the scattered procurement process. Whether purchase requests, approval workflows, or recurring SaaS payments, it allows you to automate as many procurement elements as you want.
It lets you digitize the entire process without compromising your current workflows. This boosts transparency and provides better control over your expenses.
2. Streamline Approvals

You get a no-code trigger-based approval workflow engine that helps you set exact approval hierarchies to get approvals without disruptions.
For example, you can add if-then rules and set a precise and intricate workflow. Thus, when an employee raises a purchase request, instead of chasing stakeholders, this system notifies them to review and approve the requests.
Additionally, all queries or clarifications unfold within the procurement software, ensuring comprehensive documentation and visibility. This eliminates maverick spending and fosters an accountable procurement process.
3. Vendor Management

You can sync all your vendors to your accounting software and ERPs. This creates vendor consistency across platforms, accelerating the purchase order creation. You also get the ability to add the list of items and simplify the purchase order and GRN matching process.
4. Receipt Management

You get a dedicated dashboard to manage all your receipts. The software captures invoices from emails and WhatsApp and uses OCR technology to extract key information. This streamlines GRN matching as all vendor, purchase order, and invoice details are in one place.
Pluto's procure-to-pay module is an excellent example of this centralization. It accelerates reconciliation with GL codes and tax codes, enhancing finance teams' visibility and control over purchase order spending.
5. Centralize Documentation

You have a unified information source as the software integrates with your accounting and payment software and your ERP. Hence, it becomes easy to store and maintain data while maintaining consistency across.
For instance, Pluto offers you a wide range of integrations, such as NetSuite, Xero, QuickBooks, Zoho, etc., so that you focus on procuring goods and get complete documentation with accuracy.
6. Detailed Reports

You get comprehensive reports, making it easier to extract insights and make data-driven decisions. Also, as all the information is stored within the software, there are no gaps or loss of context. You get an accurate picture of your procurement process. This allows for strategic planning and forecasting.
For instance, with Pluto, you get insights, such as average time for approvals, average payables due, top vendors, department-wise spending, location-wise spending, etc.
7. Audit Trails

Since there’s a unified platform to maintain thousands of receipts, you get complete visibility into each order from purchase requests to stakeholders involved and order status. This audit trail becomes a blessing during the audit season when you need less than 30 seconds to retrieve a specific receipt or document.
There’s More to Procurement Management than Automation
Procurement management is not just about automation. While it does enhance the three core components of procurement—people, process, and paperwork, procurement management requires more than the adoption of software.
Pluto aims not just to automate your processes but also to support your existing workflows. Then, be it purchase requests, accounts payable, or accounting, it strives to improve your processes by removing all the bottlenecks that cause chaos.
Know more about how we can help your business. Book a demo and we’ll see you across to maximize the efficiency of your procurement process.
Find out how much your business can save with Pluto
Discover your savings with Pluto's Cost Saving Calculator and take control of your expenses. Unlock cost-efficiency now!
Calculate NowLearn how Pluto is helping Keyper to eliminate petty cash spending and optimize spend management
Read More

Vlad Falin, Finance Writer
At Pluto Card, our mission is to assist businesses of all scales make well-informed choices. To uphold our standards, we follow editorial guidelines to guarantee that our content consistently aligns with our high-quality benchmarks.
Get started with a free account
Let Pluto do all the heavy lifting, so your finance team and employees can focus on things that actually matter and add to your bottom line. Get started with a free account today.
You may also be interested

•
Leen Shami
Understanding Business Expenses
All companies and businesses will incur business expenses, but how can you know what exactly is considered business expenses? And how will the introduction of UAE corporate taxes affect business expenses and income reports?
What are business expenses?
Business expenses are costs a business incurs to run the business properly. In simpler terms, they're expenses made by the business for the business.
With the UAE introducing corporate tax laws in 2023, it's crucial for businesses to be able to track and categorize their business expenses, as some of them may be tax deductible.
While the IRS may divide business expenses into ordinary and necessary business expenses, the UAE takes a different approach.
Ordinary business expenses are anything that is "common and accepted" to a business, whereas necessary expenses are anything that is "helpful and appropriate" to a business but not essential.
The federal tax authority in the UAE does not take a similar approach and only considers business expenses as tax deductible or not. We will discuss this in a later section.
- {{time-money="/components"}}
Examples of business expenses
Business expenses include a wide range of expenses, from insurance to office space, to online subscriptions, such as Zoom, Figma, or Adobe.
Let's break it down; if a design agency bills a client AED 120K per year, that doesn't mean they made a profit of 120K. When a business brings in revenue, it must account for the business expenses made to provide its clients with its services. These services include digital software subscriptions, office rent, employee wage, and/or wifi fees.
Here are some examples of the most common business expenses:
- Advertising and marketing
- Business travel (fuel, airfare, taxis, etc.)
- Employee costs (payroll, salaries, insurance, perks, etc.)
- Employee equipment (such as laptops, monitors, phones, etc.)
- Legal fees
- Office space rent & utilities
- Software subscriptions
While many more expenses are considered business expenses, these are the ones most businesses will incur.
Types of business expenses
When setting up a budgeting plan, business expenses play a vital role in keeping the businesses' financials in check. When preparing a budgeting plan, finance teams typically begin by looking at the three types of business expenses incurred.
These business expenses include:

1. Fixed expenses
Fixed costs are costs that do not change; they happen at known intervals, such as month to month.
With predictable costs, budgeting is more straightforward, as these costs are always expected and never come as a surprise.
Examples of fixed expenses include:
- Rent
- Employee payroll/salaries
- Utility bills
- Insurance
2. Variable expenses
Variable expenses are business expenses that change from month to month. These costs vary depending on a company's production or sales volume; if production or sales increase, variable expenses increase, and if production or sales decrease, variable expenses decrease as well.
Variable expenses are typically a business's largest expense, as some may be unexpected or unaccounted for.
To calculate the variable cost, multiply the quantity of the output by the variable cost per unit of output.
Total variable cost = Total quantity of output X Variable cost per unit of output
Examples of variable expenses include:
- Shipping expenses
- Sales commissions
- Raw materials (used in production)
3. Periodic expenses
Periodic expenses are business expenses that happen infrequently or, sometimes, semi-regularly.
Typically, periodic expenses happen on a quarterly or yearly basis, such as annual car insurance, but can also come as a surprise, such as a company car repair.
Budgeting can be tricky with periodic expenses, especially when expenses are infrequent.
Examples of periodic expenses include:
- Maintenance & repairs
- Merger and acquisitions costs
- Major equipment purchases
Profit and loss statement report
A profit and loss (P&L) statement, also known as an income statement, is commonly used when businesses record business expenses. Through the P&L, businesses can determine their taxable income. This is especially important for UAE businesses with an annual net income above AED 375,000.
The 3 categories of an income statement include the following:
1. Costs of goods sold (COGS)
Costs of goods sold are the costs associated with the production of goods sold by a company. This typically includes direct costs only, such as materials used and labor costs to create the goods sold. Indirect expenses are not calculated regarding COGS; these include sales and marketing.
For a business to determine gross profit, the costs of goods sold must be deducted from its revenue. They also affect how much profit a company makes on its products.
2. Operating costs
For a business to run, operating costs are unavoidable.
Generally speaking, operating costs relate to a business's daily maintenance and administration. These include costs such as COGS, payroll, rent, and overhead costs. However, non-operating costs, such as interest and investments, are excluded from an income statement.
An income statement reflects operating income after operating costs are deducted from revenue.
3. Depreciation
When accounting for depreciation, there are two types to look at:
a. Depreciation expense
A depreciation expense is a loss in value of fixed assets that companies record through depreciation. During the period you use an asset, its value decreases, and the price you originally paid for it is allocated over time.
An example would be a physical asset that loses value over time, such as a car or vehicle.
b. Accumulated depreciation
Accumulated depreciation refers to the accumulated depreciation charge a specific asset has taken as it wears down or becomes obsolete. Accumulated depreciation is shown on the balance sheet, unlike depreciation expenses reported on the income statement.
Personal and business expenses
Knowing the difference between personal and business expenses incurred is vital, especially with the UAE corporate tax law coming up. Business expenses can be used to lower a business's taxable income; however, personal expenses incurred are not considered deductible expenses.
So, what's the difference between personal and business expenses?
Personal expenses
Personal expenses are purchases made for personal reasons and cannot be used as deductible expenses.
If you make a purchase for the business but add in an item for personal use, it is crucial to have two transactions to avoid mishaps coming your way. Having two receipts will help you record and store the receipt so the business expenses can be used as deductible expenses.
Business expenses
If you're making purchases that benefit the business, such as driving more revenue, they can be considered business expenses. When making business expenses, it's essential to keep a record of the purchase by storing the receipts. By doing so, you can use these business expenses to lower your tax liability by deducting the amount from your income.
Tax deductible expenses
We've reviewed personal expenses, the 3 types of business expenses, and what goes into P&L statements. But which of these are considered tax-deductible expenses? In a nutshell, all the above, other than personal expenses. Let's delve deeper into tax-deductible expenses.
Tax deductible expenses are business expenses that help businesses generate revenue. These expenses are deducted from the company's income before applying any taxes.
Examples of tax-deductible expenses:
- Administration fees
- Advertising and marketing
- Bank charges
- Insurance
- Legal fees
- Maintenance and repair
- Office expenses
- Office rent
- Payroll/salaries
- Supplies
- Travel and transportation
- Utilities
Non-deductible tax expenses
Non-deductible tax expenses cannot be deducted from a company's income.
In the UAE, there are 3 main categories for non-deductible tax expenses:
1. Related party payments from the mainland to a Free Zone Person
The related party payments made to a Free Zone Person that is taxed at 0% on receipt of the income will not be deductible for CT purposes. However, if the payment is attributed to a mainland branch of the Free Zone Person, the related party can claim a deduction.
2. Entertainment expenses
Because these types of expenses often also have a non-business or personal element, businesses can deduct up to 50% of the expense incurred to entertain customers, shareholders, suppliers, and other business partners.
3. Other expenses
No deduction will be allowed for certain specific other expenses, such as
- Administrative penalties
- Recoverable VAT
- Donations paid to an organization that is not an approved charity or public benefit organization.
How to keep track of business expenses
To maintain your business, it's important to track your business expenses. There are several ways to track business expenses; however, you will need to establish a system to account for costs and accurately manage your business.
Here are 6 steps to keep track of your business expenses:
1. Open a business bank account
A business bank account should be completely separate from your personal checking account and must only be used for business expenses/purposes. This will help you manage your business expenses easily and give you eligibility for business credit cards or, even better, Pluto corporate cards.
2. Select an accounting system
If you haven't chosen an accounting system yet, choosing one that's appropriate for your business is vital. Some businesses opt for spreadsheet software, such as Microsoft Excel; however, to simplify the accounting process, we recommend going for accounting software that will automate the process for you.
3. Choose cash or accrual accounting
Choosing cash or accrual accounting typically depends on the size of your business.
Small businesses can use cash accounting and record transactions when they happen, as volumes are small.
For bigger businesses, accrual accounting is essential, as they have high volumes of transactions. With accrual accounting, only the product sold is recorded, rather than payment received for the product. Similarly, an expense is recorded when a bill is received rather than when an invoice is paid.
4. Store receipts
Storing receipts is essential, as they are proof of business expenses made. You can store receipts by scanning them, taking photos, and keeping digital copies.
5. Regularly manage and record expenses
It's important to track spending and categorize them accordingly. Examine every transaction to compare these business expenses to your revenue.
6. Consider subscribing to an expense software
For some businesses, it is worth looking into expense management software to automate the process of tracking, managing, and recording expenses.
Tracking business expenses with Pluto
If you choose to go for an expense management software, it will help you automate the tracking, managing, and recording of expenses. But Pluto's expense management software offers more than just tracking, managing, and recording your business expenses.
Pluto will keep detailed records of all your expenses, reduce your taxable income, and help you if you are audited or need to reconcile accounts.
With Pluto, you'll be able to do the following:
Store receipts
- Upload your receipt through Whatsapp or the Pluto app as soon as a business expense is made
- Store all digital receipts on Pluto's software

Record business expenses
- All transactions are recorded on the software automatically when using Pluto corporate cards
- Petty cash is automated, meaning expenses are recorded on the spot
- If an expense is made using an employee's personal card, the expense is recorded automatically as soon as they file for a reimbursement
Track business expenses
- All business expenses made by employees can be tracked through Pluto's dashboard
- Daily, weekly, or monthly expense reports are available in real-time

Accounting integrations
- Pluto integrates with all major accounting platforms
Auto-categorization
- All expenses recorded are auto-categorized through Pluto's AI technology
- Pluto categories are synced to your GL codes
Create tax codes
- Create and activate tax codes that sync with your accounting platform to mark expenses as tax deductible or not

Business expense FAQs
More often than not, business expenses have many different rules. Here are the commonly asked questions about business expenses:
How do I categorize expenses?
Most accounting software already has business categories incorporated in the software, so you can use them and amend them as needed.
Pluto's expense management software allows integrations with significant accounting platforms and automatically syncs to your GL codes and chart of accounts.
Do fuel costs count as business expenses?
If the fuel cost was made for business purposes, such as travel for a client meeting, then yes, it is counted as a business expense and can be considered tax deductible.
However, driving to and from work is rarely considered a business expense.
Can business expenses be carried forward?
The UAE corporate tax law details report still hasn't come out yet. We will update this question once the Federal Tax Authority shares more details in the UAE.
Is personal expenses tax deductible?
No. Personal expenses are not tax deductible.
Is my rent deductible if I am self-employed and my home is my office?
In some cases, yes, it is possible if you are self-employed, but only a certain percentage of your rent will be considered a business expense, for example, 25% of your rent.
.jpg)
•
Vlad Falin
The Complete Travel and Expense (T&E) Management Guide
Travel and expense management is crucial for ensuring that business-related travel expenses are kept in check. However the accurate collection and reporting of all travel-related expenses pose a significant challenge.
As the person in charge of managing your organization's finances, you should be obsessed with making all expense management as efficient as possible in order to save money.
But how can you simplify the travel and expense management process when there are so many moving parts and people involved? By using the right tools for the job.
In this guide, you’ll learn the importance of having a good travel and expense management policy, how to make your T&E management more efficient, and what to look for in travel and expense management software.
What is travel and expense management?
Travel and Expense (T&E) management is the process companies follow to monitor and control business travel expenses. T&E management is vital as it affects the company's financial well-being directly by ensuring all travel-related expenses are tracked for tax deduction purposes.
T&E management involves tracking and controlling expenditures such as flights, accommodation, meals, and client entertainment. Effective T&E management ensures that these costs are necessary, reasonable, and aligned with the organization's policies and goals. This management is particularly vital as travel and entertainment expenses can quickly accumulate and become significant financial commitments for businesses.
Why is travel and expense management important?
As a finance professional, you know that cost management and expense reduction are crucial aspects of financial management work. One of the ways you can do this is by tracking all deductible expenses for tax reduction purposes.
And when it comes to the hierarchy of expenses you need to keep track of, those related to corporate travel and entertainment are of particular importance.
According to Mastercard, corporate travel and entertainment expenses have become the second-highest expense category.
But not only does T&E account for a large portion of the business expenses that companies have to deal with, but it’s also been identified as the second most difficult operating cost to control.
That’s why it’s so important that your organization develops and maintains effective T&E management policies, and uses the tools available to simplify T&E management.
The challenges of travel and expense management
Managing travel and expense (T&E) can be a complex task, often fraught with a range of challenges. These challenges can significantly hinder the efficiency and effectiveness of an organization's T&E process. Key challenges include:
1. Limited Fund Access: Employees often face constraints in accessing funds for travel-related expenses, which can lead to delays and complications.
2. Security Risks: The management of expenses, especially in a digital format, raises concerns regarding data security and the risk of financial fraud.
3. Outdated Policies: An organization's T&E policies may become obsolete or fail to align with current business needs and practices, leading to inefficiencies and policy breaches.
4. Lost Reports: Misplaced or lost expense reports can disrupt the reimbursement process, leading to employee dissatisfaction and administrative headaches.
5. Inefficient Bookkeeping: Manual and outdated bookkeeping methods can result in errors and inefficiencies, making it difficult to track and manage expenses accurately.
6. Lack of Spending Visibility: Without clear visibility into T&E spending, organizations struggle to control costs and make informed budgetary decisions.
7. Slow Reimbursement Process: Delays in processing reimbursements can demotivate employees and hinder efficient financial management.
How to make travel and expense management process efficient
1. Review your travel expenses and reimbursements
One of the first things you should do is take a look at your current travel expenses to see if there are any changes to be made.
Business travelers will always need to take trips, but perhaps there are some interactions that could be handled via videoconferencing.
You can also look for ways to minimize the expenses that need to be reimbursed. For instance, by using Pluto corporate cards, you could help eliminate, or at least reduce, the need to reimburse food expenses while giving you better control over them.
2. Examine your travel policy and keep it simple
If you are having trouble with your T&E management, you should take a look at your current travel policies (and if you don’t have one already, you should make that your top priority).
Your T&E policies need to strike a balance between flexibility and strictness. Too flexible and you create waste; too rigid and you limit the ability for people to do their jobs.
A good T&E policy should include the following:
- How travel will be booked
- The process to follow for reimbursement (including what type of supporting documentation is necessary, due dates, and other stipulations).
- Any budget or spending limits, including the specific transportation methods or hotels that can be used.
- Meal allowances.
And you want to keep your policy simple and easy to read. Minimize the jargon, use short paragraphs, and a simple format with bullet points, tables, and clear headings.
You should continuously review your expense policy, particularly as your business expands, to ensure that it’s aligned with any changes in your organization.
3. Go paperless
Your team should be able to access your expense policy from anywhere and at any time. But more than that, you should aim to digitize the expense report process as much as possible.
For instance, implement the ability to submit digital expense reports and capture receipts digitally. Not only will this allow you to get a clearer view of your operations at all times, but it will help simplify your bookkeeping and easily manage receipts.
Pluto has this function!

4. Use travel expense management software
Through effective use of travel and expense management systems, you can consolidate the different scaffolds in your expense process, automate them, and eliminate time-consuming approvals while minimizing, or outright eliminating, human error.
Using Pluto allows you to cut a lot of the fat out of the reimbursement process. Automate reports, data gathering, and approvals for expenses that meet your policies, leaving only those that don’t meet your policies for manual approval.
Furthermore, it can help you detect fraud by auditing your reports for duplicate expenses and any other anomalies.
And through software integration, you can use these different tools to create a unified T&E management process.
5. Top solutions for travel and expense management
There are many tools you can use to make your T&E management more efficient, for instance:
- Pluto Card allows you to issue unlimited virtual cards, create travel specific card limits monitor spending in real-time and most importantly, it allows your employees to reimburse quickly!
- A travel expense tracker can provide you with automated expense reporting and expense tracking.
- You can use a travel management platform that allows your employees to book flights, trains, and hotels and even rent cars from one place.
- Pluto mobile app makes the expense reporting process much simpler for your employees.
- You could take data from Pluto and travel management system directly into your accounting platform to further automate and simplify the T&E management process.
Expense management software for T&E management
One of the best ways to simplify your travel and expense management is by making use of the right T&E management software. However, with the increasing amount of options available, knowing which one fits your company best can be difficult.
Since no two businesses are exactly the same, there won’t be a one-size-fits-all solution. Having said that, you’ll have an easier time choosing between the different options by focusing on the specific features that you need, or at least should consider, in a T&E management platform.
Key features to look for in a travel and expense management software
1. Virtual cards
Pluto gives you the ability to create virtual cards for online purchases. These cards can be generated as single-use or recurring, giving you complete control in terms of how you set up your spending limits.
Virtual cards offer you similar benefits to corporate cards, in the sense that you get full visibility of your expenses and your employees don’t have to pay upfront, but they have the added benefit of being more customizable.
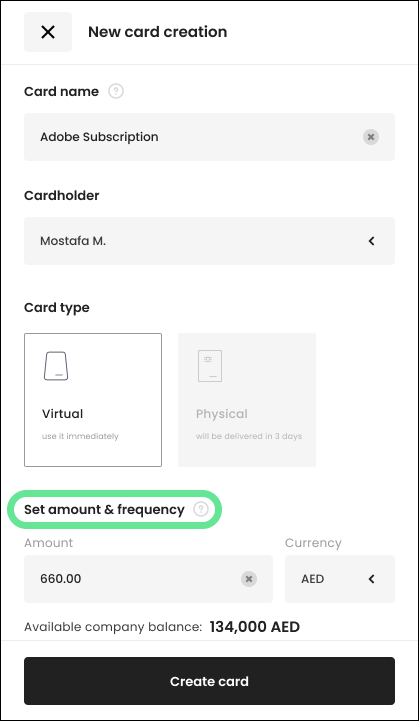
2. Flexible spending limits
Our expense management software can also give you a lot of control and flexibility over the spending limits that you set. Pluto allows you to set specific spending-limits for vendor and change them in real-time online.
This allows you to track expenses for specific countries or cities, while removing the need to manually configure spending limits each time someone makes a trip request.
3. Expense reports and analytics
If you want to make your expense management more efficient, you’ll need accurate data and insights into the spending habits of your employees.
Pluto gives you real-time reporting and analytics, to give your finance teams an easier time combing through all the expense data. For instance, a system with robust reporting capabilities should:
- Categorize expenses and organize reports by expense type
- Reconcile your reports
- Give you spending insights across all your departments
- Keep track of violations of your expense policies
- Provide you with real time spend visibility
By getting a clear picture of your expenses, you’ll have an easier time ensuring policy compliance, preventing fraud, and reducing travel costs.

4. No FX fees and multi-currency functionality
If your employees travel internationally frequently, you’ll want a product that comes with a card that doesn’t have additional fees or surcharges for international purchases.
At Pluto we have 0 FX fees. Furthermore, you’ll have an easier time managing these expenses due to multi-currency functionality automatically converting all transaction information to your country’s currency.
5. Mobile functionality
If you are trying to simplify your expense reporting process for travel expenses, then you need a way to work on those expenses on the go. Pluto’s mobile app would allow your employees to report their expenses right away from any location, while also giving them the ability to submit receipts digitally.
6. Integrated card management
If you opt for a software provider that also offers corporate credit card services, you’ll be able to automatically reconcile expense report entries with your card statements, detect any expense bottlenecks, and generally reduce the chances of fraud or misuse.
Pluto card management software will also give you more control over your corporate spending. Plus, you’ll be able to set and control your spending limits with much more ease.
7. Compatibility with other tools
When it comes to the use of technology in expense management, the more, the merrier.
Pluto can be integrated with your accounting software so that it can automatically populate expense reports and simplify your reimbursement through the use of your organization's accounting data.
Furthermore, by integrating your TEM system with your travel management system you can instantly take the travel booking information and add it to your expense reports.
8. Automated workflows, expense categorization, and tax calculation
The entire point of using travel expense management software is to automate as many processes as possible.
This includes the ability to customize your travel policies and approval workflows, categorize expenses for more straightforward tax calculation, and determine whether they are tax deductible or not.
Furthermore, by categorizing your expenses, you’ll have an easier time complying with the tax regulations of your country.
9. Scalability
One feature that is sometimes overlooked in software platforms is the ability to scale your operations as your company grows. You don’t want to choose a system now only to realize it no longer meets your needs further down the line.
In this regard, Pluto is a great pick as we have the backend to support any business sidez from small teams to enterprise level accounts.
Key takeaways
Effective expense management is all about visibility, flexibility, control, and automation. The most common pain points from T&E management come from outdated policies and manual inputs, which you should seek to update and simplify via means of a robust expense management platform.
When it comes to making your travel and expense management more efficient, the key things to remember are:
- Review and update your policy continuously to ensure it meets the needs of your business and employees.
- Examine your current expenses to look for opportunities to reduce reimbursements and consolidate expenses.
- Use Pluto to automate approval workflows and simplify the expense reporting process.
- Pluto also offers strong reporting capabilities, gives you a lot of flexibility for spending limits, and can be integrated with other tools for maximum effectiveness.

•
Mohammed Ridwan
Guide to Accounts Payable Audit With Step-by-Step Process and Checklist
Your employee receives the vendor invoice and goes to the department manager and procurement department for three-way matching — invoice, purchase order, and goods receipt. Once approved, the finance department prepares to clear the payment. Finally, the accounting department makes the journal entries and updates accounting records. This is an end-to-end accounts payable process.
But it isn't as simple and straightforward. The chances of errors increase with various stakeholders involved. These range from manual data entry mistakes and invoice duplications to missed discounts, late payments, and inaccurate coding. This intricate process further results in unapproved invoices, incomplete documentation, vendor communication gaps, and mismatched purchase orders.
Hence, it becomes imperative to conduct regular checks. The inspections look into the internal processes to identify loopholes and act as an early sign. This post will discuss what an accounts payable audit is and how you can prepare for it.
{{less-time-managing="/components"}}
What is an Accounts Payable Audit?
An accounts payable (AP) audit is a type of accounting audit that investigates a company's accounts payable records, statements, and processes for potential errors, fraud, and non-compliance.
In an AP audit, auditors track AP transactions from beginning to end, including the purchase order, invoice, approval steps, payment, and reconciliation, ensuring that everything has been recorded and documented correctly.
The auditors assess the internal records and documentation for the following:
- Validity - Are all invoices and transactions verified as genuine, preventing payment for unauthorized items?
- Completeness - Are the invoices, purchase orders, and delivery receipts recorded correctly to avoid missing any payments?
- Accuracy - Is every invoice amount cross-checked against corresponding purchase orders and delivery receipts to prevent payment errors?
- Compliance - Are the accounts payable documents compliant with tax and company policies to avoid penalties and ensure ethical financial practices?
Further, the auditors inspect the internal processes for the following:
- Segregation of Duties -Are responsibilities clearly divided to prevent conflicts and maintain a system of checks and balances
- Approvals - Are transaction approval processes in place, ensuring compliance with policies and accountability?
- Access Controls - Are access controls effectively implemented to protect sensitive information, preventing unauthorized access and potential breaches?
By addressing these questions, the auditors find areas to improve and strengthen the accounts payable system. This process provides a thorough picture of financial operations, identifying weaknesses that could affect accuracy, efficiency, and compliance.
How to Conduct an Accounts Payable Audit
Before establishing an audit plan, you need three things to prepare for an accounts payable audit:
1. Stakeholder Input
Schedule meetings with key stakeholders such as finance managers, approvers, and document handlers. Ask for their insights on pain points, challenges, and expectations related to the accounts payable process. Document their feedback and use it to tailor the audit plan. It helps to address specific concerns and improve efficiency.
2. Documents Repository
Conduct a comprehensive review of the current document storage system. Ensure all relevant documents are organized, labeled, and stored in a secure, easily accessible location. If you are using digital AP software for the repository, validate that it has proper version control and is updated.
Checklist of Documents Required
- Vendor Invoices
- Purchase Orders
- Goods/Services Receipts
- Vendor Contracts and Agreements
- Payment Records
- Expense Reports
- Vendor Statements
- Credit Memos
- Internal Controls and Policies
- General Ledger Entries
- Tax Documents
- Bank Reconciliation Statements
- Vendor Information
- Access Logs
- Expense Allocation Documentation
- Documentation of Disputed Invoices
- Employee Authorization Forms
- Proof of Payment
- Inventory Records (if applicable)
- Regulatory Compliance Documentation
3. Access Control
Review and update access controls to restrict access to sensitive financial data. Work with IT and security teams to ensure only authorized personnel can access critical systems and repositories. Also, periodically verify user access levels and promptly revoke access for individuals who no longer require it. This helps maintain a secure and controlled environment.
4-Step AP Audit Procedure
With all the documents ready, inputs gathered, and access shared, you can initiate the AP audit procedure. It includes the following steps:
Audit Plan
Establish an audit plan to define the scope of the audit, specifying the departments and time frame under consideration. Assign audit team members and allocate necessary resources for the audit. Identify potential risks such as errors or compliance issues.
Here is what an audit plan looks like.
Audit Plan
Objective: The primary aim of this audit is to express an opinion on the fairness of XYZ Company's financial statements in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
Scope: The audit will cover the financial statements of XYZ Company for the year ended December 31, 20XX, including the balance sheet, income statement, statement of cash flows, and accompanying notes.
Audit Team: The audit team will consist of the lead auditor, staff auditors, and specialists as needed. The team members will be assigned specific tasks based on their expertise and the areas to be audited.
Audit Approach: The audit will be conducted as per the auditing standards and guidelines issued by the relevant regulatory bodies. The approach will include substantive testing, tests of controls, analytical procedures, and other audit procedures as deemed necessary.
Materiality Threshold: The materiality threshold for the financial statements is set at $XXX. Any misstatements or discrepancies exceeding this threshold will be considered material.
Risk Assessment: The audit team will conduct a risk assessment to identify and assess the risks of material misstatement in the financial statements. The evaluation will consider both inherent and control risks.
Audit Procedures:
- Cash and Cash Equivalents:
- Confirm bank balances and reconciliations
- Test cash transactions and cutoff procedures
- Review bank statements and related agreements
- Revenue Recognition:
- Test sales transactions and revenue recognition policies
- Review contracts and agreements for completeness and accuracy
- Verify the accuracy of recorded revenue
- Inventory:
- Observe the physical inventory count
- Test inventory valuation methods
- Review inventory turnover and obsolescence
- Accounts Payable:
- Confirm outstanding payables with vendors
- Test completeness and accuracy of recorded payables
- Review payment terms and agreements
- Fixed Assets:
- Verify the existence and valuation of fixed assets
- Test depreciation calculations
- Review additions and disposals
Documentation: All audit procedures, findings, and conclusions will be documented in working papers, including supporting evidence and references to applicable accounting standards.
Reporting: A draft of an audit report will be prepared for management review before issuing the final report. The report will include the auditor's opinion on the financial statements and any relevant disclosures.
Fieldwork
With the audit plan in place, the audit team moves on to a detailed examination of the accounts payable process. Simultaneously, it also engages with key stakeholders to get valuable insights into the practical aspects of the AP process. In this stage, it ascertains the effectiveness of internal processes in safeguarding against potential risks. It performs the following assessments:
- Verify completeness and accuracy of invoices, purchase orders, and payment records
- Match invoices with purchase orders and delivery receipts
- Check for discrepancies in amounts or quantities
- Evaluate the adherence of the approval process to established policies
- Confirm proper authorization before payment processing
- Review vendor master file for accuracy and up-to-date information
- Implement checks to identify and rectify duplicate payments
- Ensure compliance with internal policies, industry regulations, and legal requirements
- Review accruals and prepaid expenses for accurate reflection of the financial statements
- Verify the accuracy of data entry in the financial system
However, an audit team struggles the most with finding the proper documents. Either the internal team fails to provide the specific invoices, purchase requests, and purchase orders, or it gets lost in the pile of documents. This slowdown in the audit process increases the risk of oversight and incomplete scrutiny, compromising accuracy and thoroughness.
The best way to fix this leak is to go for accounts payable automation.
With AP automation, you streamline approvals and payments and create a centralized hub for bookkeeping. Instead of manual record-keeping, the tool automatically captures and extracts all necessary documents. Its integration capabilities ensure consistent data across the organization, simplifying data management and retrieval.
Audit Report
Finally, the audit team prepares a detailed audit report, including an executive summary, methodology, findings, and recommendations. The report provides a comprehensive overview, detailing identified issues and areas of strength.
To read an audit report and implement it effectively, follow these steps:
- Involve the audit committee, executive director, and senior financial staff in reviewing the report.
- Identify significant issues, such as financial conflicts of interest, and address them promptly. Classify minor concerns, such as operational inefficiencies and technological deficiencies, for resolution over several months.
- Consider the list of best practices and custom recommendations provided by the auditors. Use them to plan and prioritize your organization's next steps.
- Evaluate the "scope, nature, and timing" of the audit conducted by the audit team to assess the auditors' efficiency in utilizing resources without redundancy. Explore ways to make the audit process more efficient for the next cycle.
Regardless of the audit cycle, continuously assess and improve auditing procedures. Explore options such as accounts payable automation, process optimizations, and strategic partnerships.
Follow-up
During this stage, the audit team monitors the implementation of recommended changes. It involves continuous communication with stakeholders to address concerns or questions arising from the audit report. The team also ensures that the proposed improvements are effectively integrated into the organization's processes.
Preparing for Your Next Accounts Payable Audit
To make your next audit easier for the auditors and the internal team, address past findings and consider adopting accounts payable automation for efficiency. By addressing previous audit issues, you proactively improve your internal processes by resolving identified issues. It builds a culture of accountability and responsibility, laying the groundwork for a more efficient and effective audit process in the future.
An AP automation software becomes a central hub for the documentation, streamlining the intricate process. Automated document capture and retrieval ensure swift access, minimizing errors. Also, it highlights areas for improvement, enabling the team to address issues beforehand.
As a result, audits become more streamlined, faster, and less stressful, ensuring strict adherence to rules and optimal functionality. We have curated a list of top AP automation software to help you pick the right one. Check the top 7 accounts payable automation solutions that simplify the accounts payable process and audits.
Modern finance teams save time & money with Pluto.
Get started today
Join 2000+ finance professionals keeping up to date with the latest news & releases.
© Pluto Card is a Pluto Financial Services Inc. company 2024
The product and services mentioned on this webpage belong to Pluto Technologies Ltd (Pluto), a company incorporated under the laws of Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), Dubai holding commercial license number CL5294. Pluto is a financial technology provider and not a bank. Pluto provides certain facilities for the utilization of payment services through Nymcard Payment Services LLC under the applicable payment network and Bank Identification Number Sponsorship of Mashreq Bank PSC. This is pursuant to the license by Visa® Inc and is available for the residents of UAE subject to Terms and Conditions of use



